A college physics blog for high school students, college students and people interested in physics. Physics blog provides online lectures, quizzes, tests, homework problems, solved solutions, for Physics 101. Download free College Physics 8th and 9th Editions assignments referencing Serway, and his related physics college textbooks. Solutions Manual for College Physics by Serway are also referenced. Physics 7th Edition Paul E. Tippens Solutions.
Tuesday, December 4, 2012
Vector quantities are represented in terms of their magnitude and direction.
Exam Review I
Name___________________________________
TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false.
1) Vector quantities are represented in terms of their magnitude and direction. 1)
2) If A+ B=0, then the vectors A and B have equal magnitudes and are directed in the same
direction.
2)
3) Free fall is the motion of an object subject only to the influence of gravity. 3)
4) If A+ B= C and A+B=C, then the vectors A and B are oriented perpendicular relative to one
other.
4)
5) The horizontal component of the velocity of a projectile remains constant during the entire
trajectory of the projectile.
5)
6) A ball is thrown at an angle of Ό above the horizontal. If there is no acceleration due to gravity the
ball will follow a straight-line path.
6)
7) An object thrown downward does not experience free fall. 7)
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
8) If a vector A has components Ax > 0, and Ay > 0, then the angle that this vector makes with the
positive x-axis must be in the range
8)
A) 0° to 90°.XXX
B) 90° to 180°.
C ) 180° to 270°.
D) 270° to 360°.
E) cannot be determined without additional information
9) You drive 6.00 km at 50.0 km/h and then another 6.00 km at 90.0 km/h. Your average speed over
the 12.0 km drive will be
9)
A) exactly 38.0 km/h.
B) greater than 70.0 km/h.
C ) less than 70.0 km/h.XXX
D) equal to 70.0 km/h.
E) cannot be determined from the information given, must also know directions traveled
10) When is the average velocity of an object equal to the instantaneous velocity? 10)
A) only when the velocity is constantXXX
B) only when the velocity is increasing at a constant rate
C ) only when the velocity is decreasing at a constant rate
D) n e v e r
E) a l w a y s
111) Suppose that an object is moving with a constant velocity. Make a statement concerning its
acceleration.
11)
A) The acceleration must be constantly increasing.
B) The acceleration must be equal to zero.XXX
C ) The acceleration must be constantly decreasing.
D) The acceleration must be a constant non-zero value.
E) A statement cannot be made without additional information.
12) The slope of a tangent line at a given time value on a velocity versus time graph gives 12)
A) displacement.
B) instantaneous velocity.
C ) instantaneous acceleration.XXX
D) average acceleration.
E) average velocity.
13) An object is moving with constant non-zero velocity in the +x-axis. The position versus time
graph of this object is
13)
A) a vertical straight line.
B) a straight line making an angle with the time axis.XXX
C ) a p a r a b o l i c c u r v e .
D) a hyperbolic curve.
E) a horizontal straight line.
14) The area under a curve in a velocity versus time graph gives 14)
A) distance traveled.
B) acceleration.
C ) velocity.
D) displacement.XXX
E) speed.
15) Two athletes jump straight up. John has twice the initial speed of Harry. Compared to Harry, John
jumps
15)
A) four times as long.XXX
B) 1.41 times as long.
C ) three times as long.
D) 0.50 times as long.
E) twice as long.
16) You drop a stone from a bridge to the river below. After this stone has traveled a distance d, you
drop a second stone. The distance between the two stones will always
16)
A) increases at first, but then stays constant.
B) increases.XXX
C ) decreases at first, but then stays constant.
D) decreases.
E) stays constant.
2FIGURE 2-6
17) Refer to Figure 2-6. If you start from the Bakery, travel to the Cafe, and then to the Art Gallery,
what is the magnitude of your displacement?
17)
A) 10.5 km
B) 6.5 km
C ) 1.5 km
D) 2.5 kmXXX
E) 9.0 km
18) A car is making a 12-mile trip. It travels the first 6.0 miles at 30 miles per hour and the last 6.0
miles at 60 miles per hour. What is the car's average speed for the entire trip?
18)
A) 45 mph
B) 20 mph
C ) 5 0 m p h
D) 35 mph
E) 40 mphXXX
FIGURE 2-7
19) Figure 2-7 represents the position of a particle as it travels along the x-axis. What is the average
speed of the particle between t = 1 s and t = 4 s?
19)
A) 0.50 m/s
B) 1.3 m/sXXX
C ) 0.25 m/s
D) 1.0 m/s
E) 0.67 m/s
3FIGURE 2-9
20) Figure 2-9 represents the velocity of a particle as it travels along the x-axis. What is the average
acceleration of the particle between t = 1 second and t = 4 seconds?
20)
A) 2.0 m/s2
B) 3.0 m/s2
C ) 1.7 m/s2X X X
D) 0.33 m/s2
E) 2.5 m/s2
FIGURE 2-10
21) Figure 2-10 shows the velocity-v e r s u s-time graph for a basketball player traveling up and down
the court in a straight-line path. Find the net displacement of the player for the 10 s shown on the
g r a p h .
21)
A) 18 mXXX B) 14 m C ) 12 m D) 20 m E) 16 m
22) An airplane starts from rest and accelerates at 10.8 m/s2. What is its speed at the end of a 400
m-long runway?
22)
A) 37.0 m/s
B) 93.0 m/sXXX
C ) 4320 m/s
D) 186 m/s
E) 65.7 m/s
423) A car is traveling at 30.0 m/s when the driver suddenly applies the brakes, giving the car a
constant deceleration. The car comes to a stop in a distance of 120.0 m. What was the deceleration
of the car?
23)
A) 4.25 m/s2
B) 4.75 m/s2
C ) 4.00 m/s2
D) 4.50 m/s2
E) 3.75 m/s2X X X
24) Car A is traveling at 22.0 m/s and car B at 29.0 m/s. Car A is 300 m behind car B when the driver of
car A accelerates his car with an acceleration of 2.40 m/s2. How long does it take car A to overtake
car B?
24)
A) 12.6 s
B) 5.50 s
C ) 19.0 s X X X
D) 316 s
E) Car A never overtakes car B.
25) An object is thrown upwards with a speed of 14 m/s. How high above the projection point does it
reach?
25)
A) 20 m B) 25 m C ) 10 mXXX D) 5.0 m E) 15 m
26) An object is thrown upwards with a speed of 14 .0 m/s. How long does it take it to reach its
maximum height?
26)
A) 1.22 s B) 3.14 s C ) 1.43 sXXX D) 5.31 s E) 4.15 s
27) An astronaut stands by the rim of a crater on the moon, where the acceleration of gravity is 1.62 m/
s2. To determine the depth of the crater, she drops a rock and measures the time it takes for it to
hit the bottom. If the depth of the crater is 120 m, how long does it take for the rock to fall?
27)
A) 3.04 s B) 32.1 s C ) 12.2 sXXX D) 37.5 s E) 29.3 s
28) The national debt is measured in trillions of dollars. Which of the following is a representation of a
trillion?
28)
A) 1 × 103
B) 1 × 109
C ) 1 × 1015
D) 1 × 106
E) 1 × 1012 XXX
29) If you are measuring the length of a room, the most appropriate SI unit is the 29)
A) centimeter.
B) meter.XXX
C ) micrometer.
D) millimeter.
E) kilometer.
530) When multiplying several quantities, the number of significant digits in the result must always be 30)
A) equal to the number of significant digits in the least accurate of the quantities.XXX
B) larger than the number of significant digits in the most accurate of the quantities.
C ) smaller than the number of significant digits in the least accurate of the quantities.
D) equal to the number of significant digits in the most accurate of the quantities.
E) equal to the average number of significant digits in the most and least accurate of the
q u a n t i t i e s .
31) What is the conversion factor between km/h and m/s? 31)
A) 2.78 × 10-1 m / s X X X
B) 3.60 m/s
C ) 7.72 × 10-5 m/s
D) 16.7 m/s
E) 1.30 × 104 m/s
32) A vector quantity is defined as 32)
A) a quantity that is specified by a numerical value only.
B) a quantity that is specified by using both a numerical value and a direction.XXX
33) The density of a solid object is defined as the ratio of the mass of the object to its volume. The
dimension of density is
33)
A) [M][L].
B) [M][ L ]-3.XXX
C ) [M][L][T].
D) [M]/[L].
E) [ L ]3/[M].
34) How many significant figures are in 10,002? 34)
A) 5XXX
B) 3
C ) 2
D) 4
E) a m b i g u o u s
35) A train travels at a constant speed of 60.4 miles per hour for 101.5 minutes. What distance does the
train cover?
35)
A) 102 milesXXX
B) 100 miles
C ) 102.2 miles
D) 102.181 miles
E) 102.18 miles
36) The Hoover Dam is 726 feet high. What is its height in kilometers? 36)
A) 0.221 kilometersXXX
B) 0.138 kilometers
C ) 0.525 kilometers
D) 0.726 kilometers
E) 0.275 kilometers
6FIGURE 3-3
37) Refer to Figure 3-3. Three forces F1 = F2= F3= 70 N are acting on an object O as shown in the
figure. Which one of the following statements is true regarding the resultant force acting over the
object O?
37)
A) The resultant force is zero.XXX
B) The resultant force is 35 N.
C ) The resultant force is 140 N.
D) The resultant force is 210 N.
E) The resultant force is 70 N.
38) Vector A = 6.0 m and points 30° north of east. Vector B = 4.0 m and points 30° west of north. The
resultant vector A + B is given by
38)
A) 9.8 m at an angle 26° north of east.
B) 9.8 m at an angle 64° east of north.
C ) 7.2 m at an angle 26° east of north.XXX
D) 3.3 m at an angle 26° north of east.
E) 3.3 m at an angle 64° east of north.
39) What is the smallest number of vectors that can be added to give a zero resultant? 39)
A) 2XXX
B) 3
C ) 4
D) 5
E) You cannot add vectors and obtain a zero resultant.
40) The eastward component of vector A is equal to the westward component of vector B and their
northward components are equal. Which one of the following statements is correct for these two
v e c t o r s ?
40)
A) Vector A is perpendicular to vector B .
B) Magnitude of vector A is equal to the magnitude of vector B .XXX
C ) Magnitude of vector A is twice the magnitude of vector B.
D) Vector A is parallel to vector B .
E) Vector A is anti-parallel to vector B .
741) Vector A = 6.0 m and points 30° south of east. Vector B = 4.0 m and points 30° east of south. The
resultant vector A + B is given by
41)
A) 4.7 m at an angle 42° south of east.
B) 1.1 m at an angle 42° south of east.
C ) 13.7 m at an angle 42° south of east.
D) 0.7 m at an angle 42° south of east.
E) 9.7 m at an angle 42° south of east.XXX
42) Vector A = 8.0 m and points east, Vector B = 6.0 m and points north, and vector C = 5.0 m and
points west. The resultant vector A + B + C is given by
42)
A) 3.8 m at an angle 67° north of east
B) 2.0 m at an angle 63° north of east.
C ) 6.7 m at an angle 63° north of east.XXX
D) 6.7 m at an angle 63° east of north.
E) 2.0 m at an angle 63° east of north.
FIGURE 3-5
43) Refer to Figure 3-5. The components of the sum of these vectors are given by
choice x-component y-component
1
2
3
4
5
0 c m
-3.5 cm
+3.5 cm
0 c m
0 c m
+6.0 cm
-2.0 cm
-2.0 cm
-4.0 cm
-2.0 cm
43)
A) Choice 1
B) Choice 2
C ) Choice 3
D) Choice 4XXX
E) Choice 5
8FIGURE 3-7
44) The magnitudes of the four vectors shown in Figure 3-7 are given as follows: A = 10.0 m, B = 8.0
m ,
C = 6.0 m, and D = 2.0 m. The components of the vector sum of these four vectors are
Choice x-component y-component
1
2
3
4
5
1.5 m
13.5 m
3.5 m
-2.9 m
18.1 m
6.0 m
20.0 m
14.0 m
-14.0 m
-5.0
44)
A) Choice 1
B) Choice 2
C ) Choice 3XXX
D) Choice 4
E) Choice 5
45)
^ ^
^ ^
A car is moving with a velocity (3.0 m/s)x + (1.0 m/s)y and 3.0 seconds later its velocity is (6.0 m/s)
x - (3.0 m/s)y. What is the direction of the average acceleration of the car?
45)
A) -53° from the x-axisXXX
B) 67° from the x-axis
C ) -67° from the x-axis
D) 53° from the x-axis
E) 60° from the x-axis
46)
^ ^ ^ ^
Vector A = 2.00 x + -1.00 y and vector B = 3.00 x + 4.00 y. What is vector C = A - B? 46)
A)
^ ^
-1.00 x + -3.00 y
B)
^
^
^
1.00 x + 3.00 y
C )
^ ^
1.00 x + 5.00 y
D)
^ ^
-1.00 x + -5.00 yX X X
E)
^ ^
-1.00 x + 3.00 y
9FIGURE 3-9
47) Refer to Figure 3-9. The components of the sum of these vectors are given by
Choice x-component y-component
1
2
3
4
5
4.9 cm
2.8 cm
0 c m
-4.2 cm
0 c m
2.8 cm
4.9 cm
4.2 cm
0 c m
4.2 cm
47)
A) Choice 1
B) Choice 2
C ) Choice 3XXX
D) Choice 4
E) Choice 5
48) If the acceleration vector of an object is directed parallel to the velocity vector, 48)
A) the object is not moving.
B) the object is speeding up.XXX
C ) the object is turning.
D) the object is slowing down.
E) this situation would not be physically possible.
49) A rock is thrown at some angle above the horizontal with a certain velocity. It reaches its highest
point and starts falling down. What is the velocity of the rock at the highest point of its trajectory?
49)
A) 0
B) 9.8 m/s
C ) It is equal to its initial velocity.
D) It is equal to its initial vertical velocity.
E) It is equal to its initial horizontal velocity.XXX
50) A boy kicks a football with an initial velocity of 20 m/s at an angle of 25° above the horizontal. The
magnitude of the acceleration of the ball while it is in flight is
50)
A) 0 m/s2.
B) 25 m/s2.
C ) 9.8 m/s2.XXX
D) 20 m/s2.
E) 8.4 m/s2.
1051) If the initial speed of a projectile is doubled. 51)
A) Its range will decrease by a factor of four.
B) Its range will quadruple.XXX
C ) Its range will double.
D) Its range will be decreased by a factor of two.
E) Its range will be increased by 1.41.
52) A bullet is fired with a certain velocity at an angle Ό above the horizontal at a location where g =
10.0 m/s2. The initial x- and y-components of its velocity are 86.6 m/s and 50.0 m/s respectively.
What is the initial velocity of the bullet?
52)
A) 100 m/sXXX
B) 86.6 m/s
C ) 50.0 m/s
D) 36.6 m/s
E) 136 m/s
53) A child throws a ball with an initial speed of 8.00 m/s at an angle of 40.0° above the horizontal. The
ball leaves her hand 1.00 m above the ground. At what angle below the horizontal does the ball
approach the ground?
53)
A) 35.1° B) 65.2° C ) 38.6° D) 48.0° XXX E) 40.0°
54) An athlete competing in long jump leaves the ground with a speed of 9.14 m/s at an angle of 35.0°
above the horizontal. How long does the athlete stay in the air?
54)
A) 1.07 sXXX B) 0.535 s C ) 2.53 s D) 0.876 s E) 0.501 s
55) A child throws a ball with an initial speed of 8.00 m/s at an angle of 40.0° above the horizontal. The
ball leaves her hand 1.00 m above the ground. How far from where the child is standing does the
ball hit the ground?
55)
A) 1.22 m
B) 1.58 m
C ) 6.79 m
D) 7.46 mXXX
E) 5.14 m
56) A ball is thrown with an initial speed of 60 m/s at an angle of 30° above the horizontal. What is the
ball's horizontal displacement at the end of 4 seconds? Use g = 10 m/s2.
56)
A) 120 m B) 240 m C ) 140 m D) 210 mXXX E) 60 m
57) A person throws a ball horizontally from the top of a building that is 40.0 m high. The initial
velocity of the ball is 100 m/s. What is the horizontal distance that the ball travels before hitting the
g r o u n d ?
57)
A) 100 m B) 286 mXXX C ) 572 m D) 325 m E) 367 m
58) A ball rolls off the edge of a table with an initial velocity of 20 m/s. The height of the table above
the ground is 2.0 m. How long does it take the ball to reach the ground?
58)
A) 0.98 s B) 0.32 s C ) 0.64 sXXX D) 2.0 s E) 0.49 s
1159) A ball is thrown horizontally with an initial velocity of 40 m/s from a height of 10 m. How long
will it take for the ball to touch the ground? Use g = 10 m/s2.
59)
A) 2.4 seconds
B) 1.0 second
C ) 0.70 second
D) 1.4 secondsXXX
E) 2.0 seconds
60) For which value of Ό is the range of a projectile fired from ground level a maximum? 60)
A) 55° above the horizontal
B) 30° above the horizontal
C ) 60° above the horizontal
D) 90° above the horizontal
E) 45° above the horizontalXXX
61) A boy kicks a football from ground level with a certain initial velocity at an angle 30.0° above the
horizontal. In 2.00 seconds the ball completes its trajectory and hits the ground. What is the initial
velocity of the ball?
61)
A) 4.90 m/s
B) 19.6 m/sXXX
C ) 39.2 m/s
D) 9.80 m/s
E) 78.4 m/s
62) A ball is thrown at an angle 40.0° above the horizontal with an initial velocity of 28.0 m/s. What is
the range of the ball?
62)
A) 37.8 m
B) 59.8 m
C ) 78.8 mXXX
D) 19.6 m
E) None of the other choices is correct.
12
Sunday, December 2, 2012
Physics Acceleration Deceleration Problems
1. A car is traveling at 26.0 m/s when the driver suddenly applies the brakes, giving the car a constant deceleration. The car comes to a stop in a distance of 120.0 m. How fast was the car moving when it was 60.0 m past the point where the brakes were applied?
A. 22.52 m/s B. 18.4 m/s C. 15.0 m/s D. 12.1 m/s
2. A car is traveling at 24.0 m/s when the driver suddenly applies the brakes, giving the car a constant deceleration. The car comes to a stop in a distance of 120.0 m. How fast was the car moving when it was 30.0 m past the point where the brakes were applied?
A. 7.50 m/s B. 15.0 m/s C. 23.5 m/s D. 20.8 m/s
3. A car is traveling with a constant speed when the driver suddenly applies the brakes, giving the car a deceleration of 3.50 m/s2 .The car comes to a stop in a distance of 34.0 m. What was the car's speed when it had traveled 17.0 m from the point where the brakes were applied?
A. 10.9 m/s B. 14.5 m/s C. 10.7 m/s D. 21.0 m/s
4. A car is traveling with a constant speed when the driver suddenly applies the brakes, giving the car a deceleration of 3.50 m/s2. If the car comes to a stop in a distance of 30.0 m, what was the car's original speed?
A. 10.2 m/s B. 14.5 m/s C. 2.5105 m/s D. 2.5210 m/s
5. A car traveling with velocity v is decelerated by a constant acceleration of magnitude a. It takes a time t to come to rest. If its initial velocity were doubled, the time required to stop would
A. double as well
B. Decrease by a factor of 2
C. Stay the Same
D. Quadruple.
We nned to calculate the acceleration using v^2 = v0^2 + 2*a*x..
since v = 0 then a = -v0^2/2x = -26^2/(2*120) = -2.817m/s^2
So when the car has gone 60m we find
v = sqrt(v0^2 + 2*a*x) = sqrt(26^2 + 2*(-2.817)*60) = 18.4m/s
2. Just like the one above with different numbers
3. First we find v0 using the v^2 = v0^2 + 2*a*x eqn where v = 0
we get v0 = sqrt(2*a*x) = sqrt(2*3.50*34) = 15.4m/s
So now when x = 17 we get v = sqrt(15.4^2 + 2*(-3.50)*17) = 10.9m/s
4.JUst like #3 above Solve using different numbers
5. Using v = v0 - a*t when it stops v = 0 ...so v0 = at..or t = v0/a
So if v0 is doubled then time is doubled
A. 22.52 m/s B. 18.4 m/s C. 15.0 m/s D. 12.1 m/s
2. A car is traveling at 24.0 m/s when the driver suddenly applies the brakes, giving the car a constant deceleration. The car comes to a stop in a distance of 120.0 m. How fast was the car moving when it was 30.0 m past the point where the brakes were applied?
A. 7.50 m/s B. 15.0 m/s C. 23.5 m/s D. 20.8 m/s
3. A car is traveling with a constant speed when the driver suddenly applies the brakes, giving the car a deceleration of 3.50 m/s2 .The car comes to a stop in a distance of 34.0 m. What was the car's speed when it had traveled 17.0 m from the point where the brakes were applied?
A. 10.9 m/s B. 14.5 m/s C. 10.7 m/s D. 21.0 m/s
4. A car is traveling with a constant speed when the driver suddenly applies the brakes, giving the car a deceleration of 3.50 m/s2. If the car comes to a stop in a distance of 30.0 m, what was the car's original speed?
A. 10.2 m/s B. 14.5 m/s C. 2.5105 m/s D. 2.5210 m/s
5. A car traveling with velocity v is decelerated by a constant acceleration of magnitude a. It takes a time t to come to rest. If its initial velocity were doubled, the time required to stop would
A. double as well
B. Decrease by a factor of 2
C. Stay the Same
D. Quadruple.
We nned to calculate the acceleration using v^2 = v0^2 + 2*a*x..
since v = 0 then a = -v0^2/2x = -26^2/(2*120) = -2.817m/s^2
So when the car has gone 60m we find
v = sqrt(v0^2 + 2*a*x) = sqrt(26^2 + 2*(-2.817)*60) = 18.4m/s
2. Just like the one above with different numbers
3. First we find v0 using the v^2 = v0^2 + 2*a*x eqn where v = 0
we get v0 = sqrt(2*a*x) = sqrt(2*3.50*34) = 15.4m/s
So now when x = 17 we get v = sqrt(15.4^2 + 2*(-3.50)*17) = 10.9m/s
4.JUst like #3 above Solve using different numbers
5. Using v = v0 - a*t when it stops v = 0 ...so v0 = at..or t = v0/a
So if v0 is doubled then time is doubled
Friday, November 30, 2012
Phys 102 College Physics II Name:
Phys 102 College Physics II Name: ______________________________________________
Additional Exercises on Chapter 11: Rotational Dynamics and Static Equilibrium
1) A man is holding an 8.00-kg vacuum cleaner at arm's length, a distance of 0.550 m from his shoulder. What is
the torque on the shoulder joint if the arm is horizontal?
A) 4.40 Nm B) 43.2 Nm C) 14.5 Nm D) 0 Nm E) 0.242 Nm
2) A 15.0-kg child is sitting on a playground teeter-totter, 1.50 m from the pivot. What force, applied 0.300 m on
the other side of the pivot, is needed to make the child lift off the ground?
A) 75.0 N B) 66.2 N C) 44.1 N D) 736 N E) 22.5 N
3) The drive chain in a bicycle is applying a torque of 0.850 Nm to the wheel of the bicycle. Treat the wheel as a
hoop with a mass of 0.750 kg and a radius of 33.0 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the wheel?
A) 1.06 rad/s2 B) 20.8 rad/s2 C) 3.43 rad/s2 D) 10.4 rad/s2 E) 5.20 rad/s2
4) In a lab experiment, a student brings up the rotational speed of a rotational motion apparatus to 30.0 rpm. She
then allows the apparatus to slow down on its own, and counts 240 revolutions before the apparatus comes to a
stop. The moment of inertia of the flywheel is 0.0850 kg·m2. What is the retarding torque on the flywheel?
A) 0.000278 Nm
B) 0.0425 Nm
C) 0.0000136 Nm
D) 0.159 Nm
E) 0.0787Nm
Figure 11-5
5) An 82.0 kg-diver stands at the edge of a light 5.00-m diving board, which is supported by two pillars 1.60 m
apart, as shown in Figure 11-5. Find the force exerted by pillar A.
A) 2.51 kN downwards
B) 1.71 kN downwards
C) 3.44 kN upwards
D) 1.71 kN upwards
E) 2.51 kN upwards
1Figure 11-6
6) A store's sign, with a mass of 20.0 kg and 3.00 m long, has its center of gravity at the center of the sign. It is
supported by a loose bolt attached to the wall at one end and by a wire at the other end, as shown in Figure
11-6. The wire makes an angle of 25.0° with the horizontal. What is the tension in the wire?
A) 196 N B) 464 N C) 297 N D) 232 N E) 116 N
Figure 11-7
7) A child is trying to stack two uniform wooden blocks, 12 cm in length, so they will protrude as much as possible
over the edge of a table, without tipping over, as shown in Figure 11-7. What is the maximum possible
overhang distance?
A) 8 cm B) 6 cm C) 9 cm D) 5 cm E) 7 cm
8) A 350-g air track cart on a horizontal air track is attached to a string that goes over a pulley with a moment of
inertia of 6.00 × 10-6 kg·m2 and a radius of 1.35 cm. The string is pulled vertically downward by a force of 2.50
N. What is the acceleration of the cart?
A) 5.27 m/s2 B) 3.27 m/s2 C) 6.53 m/s2 D) 7.14 m/s2 E) 4.98 m/s2
9) A 350-g air track cart on a horizontal air track is attached to a string that goes over a pulley with a moment of
inertia of 6.00 x 10-6 kg·m2 and a radius of 1.35 cm. The string is pulled vertically downward by a force of 2.50
N. What is the tension in the string between the pulley and the cart?
A) 2.50 N B) 2.29 N C) 1.74 N D) 4.58 N E) 1.85 N
210) A mass of 375 g hangs from a string that is wrapped around the circumference of a pulley with a moment of
inertia of 0.0125 kg·m2 and a radius of 26.0 cm. When the mass is released, the mass accelerates downward
and the pulley rotates about its axis as the string unwinds. What is the tension in the string?
A) 1.21 N B) 2.45 N C) 1.84 N D) 0.605 N E) 3.68 N
11) A 330-g air track cart on a horizontal air track is attached to a string that goes over a pulley with a moment of
inertia of 5.00 × 10-6 kg·m2 and a radius of 1.35 cm. A 255 -g mass hangs from the other end of the string and
is released. What is the acceleration of the cart?
A) 6.53 m/s2 B) 4.08 m/s2 C) 7.14 m/s2 D) 4.74 m/s2 E) 9.72 m/s2
12) A mass of 355 g hangs from one end of a string that goes over a pulley with a moment of inertia of
0.0125 kg·m2 and a radius of 15.0 cm. A mass of 680 g hangs from the other end. When the masses are
released, the larger mass accelerates downward, the lighter mass accelerates upward, and the pulley turns
without the string slipping on the pulley. What is the acceleration of the masses?
A) 3.82 m/s2 B) 2.00 m/s2 C) 2.87 m/s2 D) 5.74 m/s2 E) 7.78 m/s2
13) The torque required to turn the crank on an ice cream maker is 4.50 Nm. How much work does it take to turn
the crank through 300 full turns?
A) 8480 J B) 4240 J C) 2700 J D) 1350 J E) 2120 J
Figure 11-9
14) The L-shaped object shown in Figure 11-9 consists of the masses connected by light rods. How much work
must be done to accelerate the object from rest to an angular speed of 3.25 rad/s about the y-axis?
A) 374 J B) 42.2 J C) 173 J D) 27.4 J E) 86.5 J
15) A torque of 0.12 N·m is applied to an egg beater. (a) If the egg beater starts at rest, what is its angular
momentum after 0.50 s? (b) If the moment of inertia of the egg beater is 2.5 x 10-3 kg·m2 what is its angular
speed after 0.50 s?
16) A circular saw blade accelerates from rest to an angular speed of 3620 rpm in 6.30 revolutions. (a) Find the
torque exerted on the saw blade, assuming it is a disk of radius 15.2 cm and mass 0.755 kg. (b) Is the angular
speed of the saw blade after 3.15 revolutions greater than, less than, or equal to 1810 rpm? Explain. (c) Find the
angular speed of the blade after 3.15 revolutions.
3Answer Key
Testname: ADDITIONAL EXERCISES ON CHAPTER 11
1) B
2) D
3) D
4) A
5) B
6) D
7) C
8) C
9) B
10) A
11) B
12) B
13) A
14) C
15) (a) 0.060 kg·m2/s; (b) 24 rad/s
16) (a) 15.8 N·m; (b) greater than; (c) 2560 rev/min
4
Semester 1 Physics 101 Review Questions
Semester 1 Physics Review Questions
1) Consider the earth, orbiting the sun for a year. Make a comparison between the displacement and the distance the
earth travels.
2) You drive 6.00 km at 50.0 km/h and then another 6.00 km at 90.0 km/h. Your average speed over the 12.0 km
drive will be _________.
3) The slope of a line connecting two points on a position versus time graph represents the objects _______.
4) The slope of a tangent line at a given time on a position versus time graph represent the objects _________
5) The slope of a tangent line at a given time value on a velocity versus time graph gives ________.
6) Define average velocity
7) Define acceleration
8) Suppose that a car traveling to the East (+x direction) begins to slow down as it approaches a traffic light. Make
a statement concerning the direction of its acceleration.
9) The area under the curve of a velocity versus time graph gives represents the object's_________
10) A stone is thrown straight up. When it reaches its highest point, describe the velocity and acceleration of the
stone.
11) Suppose a ball is thrown straight up, reaches a maximum height, then falls to its initial height. Make a
statement about the direction of the velocity and acceleration as the ball is going up.
Figure 2-6
12) Refer to Figure 2-6. If you start from the Bakery, travel to the Cafe, and then to the Art Gallery, what is the
distance you have traveled?
Figure 2-7
13) Figure 2-7 represents the position of a particle as it travels along the x-axis. What is the magnitude of the average
velocity of the particle between t = 1 s and t = 4 s
14) In Figure 2-7 (above), at what value of t is the speed of the particle equal to zero?
Figure 2-10
15) Figure 2-10 shows the velocity-versus-time graph for a basketball player traveling up and down the court in a
straight-line path. Find the net displacement of the player for the 8 s shown on the graph.
16) For figure 2-10, find the acceleration a) from t = 0 sec to t = 2 sec b) from t = 4 sec to t = 8 sec17) An airplane starts from rest and accelerates at 10.8 m/s
2
. What is its speed at the end of a 400. m-long runway?
18) A car is traveling with a constant speed when the driver suddenly applies the brakes, giving the car a deceleration
of 3.50 m/s
2
. If the car comes to a stop in a distance of 30.0 m, what was the car's original speed?
19) An object is thrown upwards with a speed of 14.0 m/s. How long does it take it to reach its maximum height?
20) An object is thrown up with a speed of 14 m/s. How high above the projection point is it after 0.50 s?
21) To determine the height of a bridge above the water, a person drops a stone and measures the time it takes for it
to hit the water. If the time is 2.3 s, what is the height of the bridge?
22) A model rocket rises with constant acceleration to a height of 3.2 m, at which point its speed is 26.0 m/s . How
much time does it take for the rocket to reach this height?
23) A model rocket rises with constant acceleration to a height of 3.2 m, at which point its speed is 26.0 m/s . What
was the magnitude of the rocket's acceleration?
24) Which quantities that we have used this year in Physics are scalar quantities?
25) Which quantities that we have used this year in Physics are vector quantities?
26) A soccer player carries the ball for a distance of 40.0 m in the direction 42.0° west of south. Find the westward
component of the ball's displacement.
27) For general projectile motion, which statement is true when the projectile is at the highest point of its trajectory?
A) The horizontal and vertical components of its velocity are zero.
B) Its velocity and acceleration are both zero.
C) Its velocity is perpendicular to the acceleration.
D) The horizontal component of its velocity is zero.
E) Its acceleration is zero
28) A pilot drops a bomb from a plane flying horizontally at a constant speed. Neglecting air resistance, where will
the horizontal location of the plane be when the bomb hits the ground? (relative to the bomb)
29) A rock is thrown at 60° above the horizontal with a velocity of 40 m/s. It reaches its highest point and starts
falling down. What is the velocity of the rock at the highest point of its trajectory?
30) A student kicks a soccer ball in a high arc toward the opponent's goal. Neglecting air resistance, describe the
velocity and acceleration on its way up in its trajectory.
31) A bullet is fired from ground level with a speed of 150 m/s at an angle 30.0° above the horizontal at a location
where g = 10.0 m/s
2
. What is the vertical component of its velocity when it is at the highest point of its
trajectory?
32) The horizontal and vertical components of the initial velocity of a football are 16 m/s and 20 m/s respectively.
How long does it take for the football to rise to the highest point of its trajectory?
33) A ball is thrown horizontally with an initial velocity of 40 m/s from a height of 10 m. How long will it take for
the ball to touch the ground, neglecting air resistance?
34) A ball rolls over the edge of a building with a horizontal velocity 3.20 m/s. The horizontal range of the ball from
the base of the table is 20.0 m. How tall is the building, neglecting air resistance?
35) A ball is thrown with an initial speed of 60 m/s at an angle of 30° above the horizontal. What is the ball's
horizontal displacement at the end of 4 seconds?
36) A boy kicks a football from ground level with an initial velocity of 20 m/s at an angle of 60° above the
horizontal. What is the horizontal distance to the point where the football hits the ground?37) A boy kicks a football with an initial velocity of 28.0 m/s at an angle of 30.0° above the horizontal. What is the
highest elevation reached by the football in its trajectory?
38) A crow is flying horizontally with a constant speed of 2.70 m/s when it releases a clam from its beak. The clam
lands on the rocky beach 2.10 s later. Just before the clam lands, what is (a) its horizontal component of velocity,
and (b) its vertical component of velocity? (c) its resultant velocity and the angle it makes below the horizontal?
39) In the absence of an external unbalanced force, a moving object will do what as time goes on?
40) An object is moving with constant velocity. a) What can you say about the net force?
b) If there are forces acting on the object, what can you conclude about the forces?
41) When a parachutist jumps from an airplane, he eventually reaches a constant speed, called the terminal velocity.
This means what regarding forces? Draw a FBD
42) A 8000kg truck is towing a 2000kg car. The force exerted by the truck on the car is 6000 N. The force exerted by
the car on the truck is ________.
43) A 0.30 kg ball is thrown up into the air. Ignore air resistance. When it is reaches its maximum height, the net
force acting on it is _______.
44) The elevator in the Space Needle is going down. When the tension pulling up on the elevator is equal to the
elevator's weight, what happens to the motion of the elevator?
45) You ride on an elevator that is moving downward with constant speed while standing on a bathroom scale. How
does the reading on the scale compare to your true weight, mg
46) A block of mass 55kg slides down a frictionless plane inclined at an angle 17° with the horizontal. The normal
force exerted by the plane on the block is?
47) An object rests on an inclined surface. If the inclination of the surface is made steeper, what does the normal force
on the object do?
48) Two objects have masses m and 5m, respectively. They both are placed side by side on a frictionless inclined
plane and allowed to slide down from rest. It takes the heavier object _____times longer/shorter to reach the
bottom of the incline than the lighter.
49) In a particle accelerator, a proton reaches an acceleration of 9.0 x 10
13
m/s
2
. The mass of a proton is
1.7 x 10
-27
kg. What is the net force on the proton?
50) A flatbed truck is carrying a load of timber which is not tied down. The mass of the timber is 899 kg. The
maximum static frictional force between the truck bed and the load is 5488 N. What is the highest acceleration
that the truck can have without losing its load? What is the static coefficient of friction between the load and truck
bed?
51) A 1250 kg boat is pulling a 72 kg water skier on a calm lake. Friction is negligible. The boat accelerates with an
acceleration of 1.3 m/s
2
. What is the force exerted on the skier by the tow rope?
52) A 50.0 kg crate is being pulled along a horizontal frictionless surface. The pulling force is 10.0 N and is directed
20.0° above the horizontal. What is the acceleration of the crate?
53) A 40.0 kg box is being pushed along a horizontal frictionless surface. The pushing force is 15.0 N directed at an
angle of 15.0° below the horizontal. What is the normal force exerted on the crate by the ground?
54) A person has a mass of 45 kg. How much does she weigh? How much less does she weigh on the Moon, where
g = 1.62 m/s
2
?55) A 40.0-kg crate is being lowered by means of a rope. Its downward acceleration is 2.00 m/s
2
. What is the force
exerted by the rope on the crate?
56) A 36.0-kg child steps on a scale in an elevator. The scale reads 400. N. What is the direction and magnitude of
the acceleration of the elevator?
57) A tightrope walker with a mass of 60.0 kg stands at the center of a rope which was initially strung horizontally
between two poles. His weight causes the rope to sag symmetrically, making an angle of 4.80° with the
horizontal. What is the tension in the rope?
58) A 10.0 kg picture is held in place by two wires, one hanging at 50.0° to the left of the vertical and the other is
horizontal. What is the tension in the wires?
Figure 5-27
59) A skier speeds down a trail, Figure 5-27. The surface is frictionless and inclined at an angle of 22.0° with the
horizontal. Find the acceleration of the skier.
60) A 2500 kg car accelerates from 0 to 21m/s in 5.2s. What is the friction force with the road, neglecting air
resistance?
Figure 6-1
61) In Figure 6-1, the block of mass 43.6 kg is at rest on an inclined plane that makes an angle of 25.1° with the
horizontal. What is the force of static friction?
62) Bobby (61kg) and Wayne (98kg) get in a tussle on the ice in a hockey game. If Bobby pushes Wayne with a force
of 77N what is the acceleration of each backwards? Neglect friction.
63) A tired mom puts a 0.200 kg latte on the roof of her car and forgets it. The coefficient of static friction between
the cup and the roof is 0.400. What is the maximum acceleration that the car can have if the cup is to stay in
place?
64) A horse pulls a 555 kg sleigh across a level snow covered field at constant speed. The coefficient of friction, µ,
is 0.15 between the sleigh and the snow. What is the force exerted on the horse by the sleigh?
Figure 6-11
65) Two masses are connected by a string which goes over an ideal pulley as shown in Figure 6-11. Block A has a
mass of 3.0 kg and can slide along a frictionless plane inclined 30° to the horizontal. What is the mass of block
B if the system is in equilibrium?Figure 6-12
66) Refer to Figure 6-12. Block A has a mass of 3.00 kg and rests on a frictionless table and is connected to block
B, which has a mass of 2.00 kg, after passing over an ideal pulley, as shown. Block B is released from rest.
What is the acceleration of the system?
Figure 6-10
67) A 3.00-kg mass (M1
) and a 5.00-kg mass (M2
) hang vertically at the ends of a rope that goes over an ideal pulley
(Figure 6-10). If the masses are released, what is the resulting acceleration of the system?
Answers:
1. The displacement is zero, the distance is quite large.
2. less than 64.3 km/h
3. average velocity
4. instantaneous velocity
5. instantaneous acceleration
6. vav
= ∆d/∆t
7. a = ∆v/∆t
8. The car is decelerating, and its acceleration is negative
and points West (‐x direction)
9. Displacement
10. its velocity is zero and its acceleration is straight down .
11. Its velocity points straight upward and its acceleration
points straight downward
12. 10.5 km
13. 0.67 m/s
14. 3 s
15. 18 m
16. a) 2 m/s
2
b) 0 m/s
2
17. 93.0 m/s
18. 14.5 m/s
19. 1.43 s
20. 5.8 m
21. 26 m
22. 0.25 s
23. 110 m/s
2
24. mass, time, speed, distance
25. displacement, velocity, acceleration, force, weight
26. 26.8 m
27. Its velocity is perpendicular to the acceleration
28. it will be directly over the bomb
29. 20 m/s horizontal
30. Vertical velocity is decreasing at 9.81 m/s
2
, Horizontal
velocity remains constant, Acceleration is 9.81m/s
2
down.
31. 0 m/s
32. 2.0 s
33. 1.4 seconds
34. 192m
35. 210 m
36. 35 m
37. 10.0 m
38. (a) 2.70 m/s (b) ‐20.6 m/s (c) 20.8m/s, 82.5°
39. move with constant velocity
40. (a) The net force on the object is zero
(b) they are balanced
41. the force of air resistance is equal and in opposite in
direction to the weight of the parachutist
42. 6000 N, they are a third law force pair
43. equal to its weight, 2.9 N
44. The elevator continues to descend with constant speed
45. equal to your true weight, mg
46. 520N
47. decreases
48. The two objects reach the bottom of the incline at the
same time
49. 1.5 x 10
‐13
N
50. 6.10 m/s
2
, 0.622
51. 94 N
52. 0.188 m/s
2
53. 396 N
54. 440 N, 367 N less
55. 312 N
56. 1.30 m/s
2
57. 3520 N
58. 153 N in angled wire, 117 N in horizontal wire
59. 3.67m/s
2
60. 10,000 N
61. 181 N
62. Bobby 1.3 m/s
2
, Wayne 0.79 m/s
2
63. 3.92 m/s
2
64. 820N
65. 1.5 kg
66. 3.92 m/s
2
67. 2.45 m/s
2
Physics 101 Final Practice Exam
Practice FINAL EXAM
Physics 101
To get a full credit show the all calculations steps in the spaces provided. All work must be shown in order to receive FULL credit.
1) A car is traveling with a constant speed when the driver suddenly applies the brakes, giving the car a deceleration of 3.50 m/s2. If the car comes to a stop in a distance of 30.0 m, what was the car's original speed?
A) 10.2 m/s
B) 14.5 m/s
C) 105 m/s
D) 210 m/s
Answer: B
2) Two athletes jump straight up. John has twice the initial speed of Harry. Compared to Harry, John stays in the air
A) 1.41 times as long.
B) twice as long.
C) three times as long.
D) four times as long.
Answer: B
3) An astronaut stands by the rim of a crater on the moon, where the acceleration of gravity is 1.62 m/s2. To determine the depth of the crater, she drops a rock and measures the time it takes for it to hit the bottom. If the depth of the crater is 120 m, how long does it take for the rock to fall?
A) 3.04 s
B) 12.2 s
C) 29.3 s
D) 32.1 s
Answer: B
4) A car traveling with velocity v is decelerated by a constant acceleration of magnitude a. It travels a distance d before coming to rest. If its initial velocity were doubled, the distance required to stop would
A) double as well.
B) decrease by a factor of two.
C) stay the same.
D) quadruple.
Answer: D
5) Figure above represents the position of a particle as it travels along the x-axis. What is the average speed
of the A particle between t = 2 s and t = 4 s?
A) 1.0 m/s
B) 1.3 m/s
C) 0.67 m/s
D) 0.50 m/s
Answer: A
6) Figure above represents the position of a particle as it travels along the x-axis. What is the average velocity of the
particle between t = 2 s and t = 4 s?
A) 2.0 m/s
B) 1.3 m/s
C) 1.7 m/s
D) 0 m/s
Answer: D
7) To determine the height of a bridge above the water, a person drops a stone and measures the time it takes for it
to hit the water. If the height of the bridge is 41 m, how long will it take for the stone to hit the water?
A) 2.3 s
B) 2.6 s
C) 2.9 s
D) 3.2 s
Answer: C
8) A vector A has components Ax > 0, and Ay > 0, the angle that this vector makes with the positive x-axis must be
in the range
A) 0° to 90°.
B) 90° to 180°.
C) 180° to 270°.
D) 270° to 360°.
Answer: A
9) A car moves from the point (3.0 m) xˆ + (5.0 m) yˆ to the point (8.0 m) xˆ - (7.0 m) yˆ in 2.0 s. What is the
direction of the average velocity of the car?
A) 67° from the x-axis
B) -67° from the x-axis
C) 33° from the x-axis
D) -33° from the x-axis
Answer: B
10) A boy kicks a football with an initial velocity of 28.0 m/s at an angle of 30.00 above the horizontal. What is the
highest elevation reached by the football in its trajectory?
A) 11.2 m
B) 10.0 m
C) 12.7 m
D) 9.40 m
Answer: B
11) A ball rolls over the edge of a table with a horizontal velocity v m/s. The height of the table is 1.6 m and the
horizontal range of the ball from the base of the table is 20 m. What is the magnitude and direction of the ball's
acceleration right before it touches the ground?
A) 4.9 m/s2 downward
B) 0 m/s2 downward
C) 9.6 m/s2 downward
D) 9.8 m/s2 downward
Answer: D
12) A bullet is fired from ground level with a speed of 150 m/s at an angle 30.00 above the horizontal at a location
where g = 10.0 m/s2. What is the horizontal component of its velocity after 4 seconds?
A) 150 m/s
B) 0 m/s
C) 130 m/s
D) 75.0 m/s
Answer: C
13) A student kicks a soccer ball in a high arc toward the opponent's goal. At the highest point in its trajectory:
A) both velocity and acceleration of the soccer ball are zero.
B) neither the ball's velocity nor its acceleration is zero.
C) the ball's acceleration is zero but not its velocity.
D) the ball's acceleration points upwards.
Answer: B
14) A 10.0-kg picture is held in place by two wires, one hanging at 35.0° to the left of the vertical and the other at 45.0° to the right of the vertical. What is the tension in the first wire?
A) 70.4 N
B) 50.8 N
C) 98.1 N
D) 69.4 N
Answer: A
15) A 30.0-kg object slides down a slope which is inclined 27.0° to the horizontal. What is the normal force on the object?
A) 171 N
B) 262 N
C) 387 N
D) 398 N
Answer: B
16) Refer to Figure above. Block A has a mass of 3.00 kg, block B has a mass of 5.00 kg and block C has a mass of 2.00 kg. The pulleys are ideal and there is no friction between block B and the table. What is the acceleration of the masses?
A) 0.981 m/s2
B) 1.86 m/s2
C) 2.94 m/s2
D) 4.20 m/s2
Answer: A
17) A 1000-kg car is moving at 30.0 m/s around a horizontal curve whose radius is 100 m. What is the magnitude of the frictional force required to keep the car from sliding?
A) 9000 N
B) 9810 N
C) 300 N
D) 3000 N
Answer: A
18) Pulling out of a dive, the pilot of an airplane guides his plane into a vertical circle. At the bottom of the dive, the speed of the airplane is 320 m/s. What is the smallest radius allowable for the vertical circle if the pilot's apparent weight is not to exceed 7.00 times his true weight?
A) 1740 m
B) 1490 m
C) 2240 m
D) 228 m
Answer: A
19) An object is under the influence of a force as represented by the force vs. position graph in Figure above. What is the work done as the object moves from 0 m to 4 m?
A) 20 J
B) 30 J
C) 0 J
D) 40 J
Answer: A
20) An object of mass m moving in a certain direction has a kinetic energy of 4.0 J. It hits a wall and comes back with half its original kinetic energy. If the speed of the object on return is 2.0 m/s, what is the mass of the object?
A) 2.8 kg
B) 3.8 kg
C) 1.0 kg
D) 4.0 kg
Answer: C
A roller coaster of mass 80.0 kg is moving with a speed of 20.0 m/s at position A as shown in Figure. The vertical height at position A above ground level is 200 m. Neglect friction and use g = 10.0 m/s2.
21) Refer to Figure above. What is the total energy of the roller coaster at point A?
A) 16.0 × 103 J
B) 20.2 × 103 J
C) 16.0 × 104 J
D) 17.6 × 104 J
Answer: D
22) Refer to Figure above. What is the total energy of the roller coaster at point B?
A) 16.4 × 103 J
B) 20.2 × 103 J
C) 17.6 × 104 J
D) 16.4 × 104 J
Answer: C
23) A rocket is fired in a gravity-free environment in deep space. The rocket has an initial mass of 8000 kg and ejects gas with a velocity of 2000 m/s. How much gas must be ejected in the first second to give the rocket an acceleration of 30.0 m/s?
A) 120 kg
B) 7.50 kg
C) 15.0 kg
D) 150 kg
Answer: A
24) Earth's radius is 6.38 × 106 m, and it completes one revolution every day. What is the tangential speed of a person standing on the equator?
A) 232 m/s
B) 148 m/s
C) 464 m/s
D) 73.8 m/s
Answer: C
25) Neptune has a radius of 2.48 × 107 m and an escape velocity of 23,300 m/s. What is the mass of Neptune? G =
6.67 × 10-11 N•m2/kg2.
A) 1.01 × 1026 kg
B) 2.02 × 1026 kg
C) 3.03 × 1026 kg
D) 4.04 × 1026 kg
Answer: A
26) A car moving at 10.0 m/s encounters a bump that has a circular cross-section with a radius of 30.0 m. What is
the normal force exerted by the seat of the car on a 60.0-kg passenger when the car is at the top of the bump?
A) 200 N
B) 389 N
C) 789 N
D) 589 N
Answer: B
27) A 2-kg ball is moving with a constant speed of 5 m/s in a horizontal circle whose radius is 50 cm. What is the
acceleration of the ball?
A) 0 m/s2
B) 10 m/s2
C) 20 m/s2
D) 50 m/s2
Answer: D
28) A 15.0-kg child is sitting on a playground teeter-totter, 1.50 m from the pivot. What force, applied 0.300 m on
the other side of the pivot, is needed to make the child lift off the ground?
A) 75.0 N
B) 736 N
C) 44.1 N
D) 66.2 N
Answer: B
29) A figure skater is spinning slowly with arms outstretched. She brings her arms in close to her body and her
moment of inertia decreases by 1/2. By what factor does her rotational kinetic energy change?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 2
D) It doesn't change.
Answer: A
30) A fan is turned off, and its angular speed decreases from 10.0 rad/s to 6.3 rad/s in 5.0 s. What is the magnitude
of the angular acceleration of the fan?
A) 0.74 rad/s2
B) 0.37 rad/s2
C) 11.6 rad/s2
D) 1.16 rad/s2
Answer: A
Tuesday, November 27, 2012
Chapter 7 Rotational Motion Law of Gravity Quick Quizzes
1. (c). For a rotation of more than 180°,
the angular displacement must be larger than p = 3.14 rad. The angular displacements in the
three choices are (a) 6 rad - 3 rad = 3 rad, (b) 1 rad -(-1) rad = 2 rad, (c) 5 rad -1 rad = 4 rad.
2. (b). Because all angular displacements occurred in the same time
interval, the displacement with the lowest value will be associated with the
lowest average angular speed.
3. (b).
From

it is seen that the case with the smallest angular displacement involves the highest angular acceleration.
it is seen that the case with the smallest angular displacement involves the highest angular acceleration.
4. (b).
All points in a rotating rigid body have the same angular speed.
5. (a). Andrea and Chuck have the same
angular speed, but Andrea moves in a circle with twice the radius of the circle
followed by Chuck. Thus, from  , it is seen that Andrea’s tangential speed is twice Chuck’s.
, it is seen that Andrea’s tangential speed is twice Chuck’s.
6. 1. (e). Since the tangential speed is constant, the tangential
acceleration is zero.
2. (a). The centripetal acceleration,  , is inversely proportional to the radius when the tangential
speed is constant.
, is inversely proportional to the radius when the tangential
speed is constant.
3. (b). The angular speed,  , is inversely proportional to the radius when the tangential
speed is constant.
, is inversely proportional to the radius when the tangential
speed is constant.
7. (c). Both the velocity and acceleration
are changing in direction, so neither of these vector quantities is constant.
8. (b) and (c).
According to Newton’s law of universal gravitation, the force between the ball
and the Earth depends on the product of their masses, so both forces, that of
the ball on the Earth, and that of the Earth on the ball, are equal in
magnitude. This follows also, of course, from Newton’s third law. The ball has
large motion compared to the Earth because according to Newton’s second law,
the force gives a much greater acceleration to the small mass of the ball.
9. (e). From F = G Mm/r2, the gravitational force is inversely
proportional to the square of the radius of the orbit.
10. (d). The semi-major axis of the asteroid’s orbit is 4 times the size
of Earth’s orbit. Thus, Kepler’s third law (T2/r3 = constant) indicates that
its orbital period is 8 times that of Earth.
Physics 101 Quiz Momentum, Kinematics, Collisions,
1
Momentum
____ 1. A ball with original momentum +4.0 kgm/s hits a wall and bounces straight back without losing any kinetic
energy. The change in momentum of the ball is:
a. 0. c. 8.0 kgm/s.
b. 4.0 kgm/s. d. 8.0 kgm/s.
____ 2. A 75-kg swimmer dives horizontally off a 500-kg raft. The diver's speed immediately after leaving the raft is
4.0 m/s. A micro-sensor system attached to the edge of the raft measures the time interval during which the
diver applies an impulse to the raft just prior to leaving the raft surface. If the time interval is read as 0.20 s,
what is the magnitude of the average horizontal force by diver on the raft?
a. 900 N c. 525 N
b. 450 N d. 1 500 N
____ 3. A 0.12-kg ball is moving at 6 m/s when it is hit by a bat, causing it to reverse direction and have a speed of 14
m/s. What is the change in the magnitude of the momentum of the ball?
a. 0.39 kgm/s c. 1.3 kgm/s
b. 0.42 kgm/s d. 2.4 kgm/s
____ 4. Alex throws a 0.15-kg rubber ball down onto the floor. The ball's speed just before impact is 6.5 m/s, and just
after is 3.5 m/s. What is the change in the magnitude of the ball's momentum?
a. 0.09 kgm/s c. 4.3 kgm/s
b. 1.5 kgm/s d. 126 kgm/s
____ 5. Alex throws a 0.15-kg rubber ball down onto the floor. The ball's speed just before impact is 6.5 m/s, and just
after is 3.5 m/s. If the ball is in contact with the floor for 0.025 s, what is the magnitude of the average force
applied by the floor on the ball?
a. 60 N c. 3.0 N
b. 133 N d. 3.5 N
____ 6. A crane drops a 0.30 kg steel ball onto a steel plate. The ball's speeds just before impact and after are 4.5 m/s
and 4.2 m/s, respectively. If the ball is in contact with the plate for 0.030 s, what is the magnitude of the
average force that the ball exerts on the plate during impact?
a. 87 N c. 3.0 N
b. 133 N d. 3.5 N
____ 7. Jerome pitches a baseball of mass 0.20 kg. The ball arrives at home plate with a speed of 40 m/s and is batted
straight back to Jerome with a return speed of 60 m/s. What is the magnitude of change in the ball's
momentum?
a. 4.0 kgm/s c. 18 kgm/s
b. 8.0 kgm/s d. 20 kgm/s
____ 8. Lonnie pitches a baseball of mass 0.20 kg. The ball arrives at home plate with a speed of 40 m/s and is batted
straight back to Lonnie with a return speed of 60 m/s. If the bat is in contact with the ball for 0.050 s, what is
the impulse experienced by the ball?
a. 360 Ns c. 400 Ns
b. 20 Ns d. 9.0 Ns2
____ 9. A car wash nozzle directs a steady stream of water at 1.5 kg/s, with a speed of 30 m/s, against a car window.
What force does the water exert on the glass? Assume the water does not splash back.
a. 11 N c. 110 N
b. 45 N d. 440 N
____ 10. A 75-kg swimmer dives horizontally off a 500-kg raft. If the diver's speed immediately after leaving the raft is
4 m/s, what is the corresponding raft speed?
a. 0.2 m/s c. 0.6 m/s
b. 0.5 m/s d. 4.0 m/s
____ 11. A cannon of mass 1 500 kg fires a 10-kg shell with a velocity of 200 m/s at an angle of 45 above the
horizontal. Find the recoil velocity of the cannon across the level ground.
a. 1.33 m/s c. 2.41 m/s
b. 0.94 m/s d. 1.94 m/s
____ 12. A machine gun is attached to a railroad flatcar that rolls with negligible friction. If the railroad car has a mass
of 6.25 10
4
kg, how many bullets of mass 25 g would have to be fired at 250 m/s off the back to give the
railroad car a forward velocity of 0.5 m/s?
a. 400 c. 3 000
b. 2 000 d. 5 000
____ 13. Ann the Astronaut weighs 60 kg. She is space walking outside the space shuttle and pushes a 350-kg satellite
away from the shuttle at 0.90 m/s. What speed does this give Ann as she moves toward the shuttle?
a. 4.0 m/s c. 8.5 m/s
b. 5.3 m/s d. 9.0 m/s
____ 14. A miniature spring-loaded, radio-controlled gun is mounted on an air puck. The gun's bullet has a mass of
5.00 g, and the gun and puck have a combined mass of 120 g. With the system initially at rest, the radio
controlled trigger releases the bullet causing the puck and empty gun to move with a speed of 0.500 m/s.
What is the bullet's speed?
a. 4.80 m/s c. 48.0 m/s
b. 11.5 m/s d. 12.0 m/s
____ 15. A uranium nucleus (mass 238 units) at rest decays into a helium nucleus (mass 4.0 units) and a thorium
nucleus (mass 234 units). If the speed of the helium nucleus is 6.0 10
5
m/s, what is the speed of the thorium
nucleus?
a. 1.0 10
4
m/s c. 3.6 10
4
m/s
b. 3.0 10
4
m/s d. 4.1 10
4
m/s
____ 16. A 20-g bullet moving at 1 000 m/s is fired through a one-kg block of wood emerging at a speed of 100 m/s. If
the block had been originally at rest and is free to move, what is its resulting speed?
a. 9 m/s c. 90 m/s
b. 18 m/s d. 900 m/s
____ 17. A 20-g bullet moving at 1 000 m/s is fired through a one-kg block of wood emerging at a speed of 100 m/s.
What is the kinetic energy of the block that results from the collision if the block had not been moving prior
to the collision and was free to move?
a. 10 kJ c. 0.16 kJ
b. 9.8 kJ d. 0.018 kJ3
____ 18. A billiard ball is moving in the x-direction at 30.0 cm/s and strikes another billiard ball moving in the
y-direction at 40.0 cm/s. As a result of the collision, the first ball moves at 50.0 cm/s, and the second ball
stops. In what final direction does the first ball move?
a. in the x-direction c. at an angle of 45.0 ccw from the
x-direction
b. at an angle of 53.1 ccw from the
x-direction
d. Such a collision cannot happen.
____ 19. During a snowball fight two balls with masses of 0.4 and 0.6 kg, respectively, are thrown in such a manner
that they meet head-on and combine to form a single mass. The magnitude of initial velocity for each is 15
m/s. What is the speed of the 1.0-kg mass immediately after collision?
a. zero c. 6 m/s
b. 3 m/s d. 9 m/s
____ 20. A 2 500-kg truck moving at 10.00 m/s strikes a car waiting at a traffic light, hooking bumpers. The two
continue to move together at 7.00 m/s. What was the mass of the struck car?
a. 1 730 kg c. 1 200 kg
b. 1 550 kg d. 1 070 kg
____ 21. A 0.10-kg object moving initially with a velocity of +0.20 m/s makes an elastic head-on collision with a
0.15-kg object initially at rest. What percentage of the original kinetic energy is retained by the 0.10-kg
object?
a. 4% c. 50%
b. 4% d. 96%
____ 22. Two billiard balls have velocities of 2.0 m/s and 1.0 m/s when they meet in an elastic head-on collision.
What is the final velocity of the first ball after collision?
a. 2.0 m/s c. 0.5 m/s
b. 1.0 m/s d. +1.0 m/s
____ 23. Two objects, one less massive than the other, collide elastically and bounce back after the collision. If the two
originally had velocities that were equal in size but opposite in direction, then which one will be moving
faster after the collision?
a. The less massive one. c. The speeds will be the same after the
collision.
b. The more massive one. d. There is no way to be sure without the
actual masses.
____ 24. A 7.0-kg bowling ball strikes a 2.0-kg pin. The pin flies forward with a velocity of 6.0 m/s; the ball continues
forward at 4.0 m/s. What was the original velocity of the ball?
a. 4.0 m/s c. 6.6 m/s
b. 5.7 m/s d. 3.3 m/s
____ 25. Two skaters, both of mass 75 kg, are on skates on a frictionless ice pond. One skater throws a 0.3-kg ball at 5
m/s to his friend, who catches it and throws it back at 5 m/s. When the first skater has caught the returned ball,
what is the velocity of each of the two skaters?
a. 0.02 m/s, moving apart c. 0.02 m/s, moving towards each other
b. 0.04 m/s, moving apart d. 0.04 m/s, moving towards each other4
____ 26. A 90-kg halfback running north with a speed of 10 m/s is tackled by a 120-kg opponent running south at 4
m/s. The collision is perfectly inelastic. Compute the velocity of the two players just after the tackle.
a. 3 m/s south c. 2 m/s north
b. 2 m/s south d. 3 m/s north
____ 27. Popeye, of mass 70 kg, has just downed a can of spinach. He accelerates quickly and stops Bluto, of mass 700
kg (Bluto is very dense), who is charging in at 10 m/s. What was Popeye's speed?
a. 10 m/s c. 50 m/s
b. 31 m/s d. 100 m/s
____ 28. Two identical 7-kg bowling balls roll toward each other. The one on the left is moving at +4 m/s while the
one on the right is moving at 4 m/s. What is the velocity of each ball after they collide elastically?
a. Neither is moving. c. +4 m/s, 4 m/s
b. 4 m/s, +4 m/s d. 14 m/s, 14 m/s
____ 29. A 5-kg object is moving to the right at 4 m/s and collides with a 4-kg object moving to the left at 5 m/s. The
objects collide and stick together. After the collision, the combined object:
a. has the same kinetic energy that the
system had before the collision.
c. has no kinetic energy.
b. has more kinetic energy than the system
had before the collision.
d. has less momentum than the system had
before the collision.
____ 30. A model car is propelled by a cylinder of carbon dioxide gas. The cylinder emits gas at a rate of 4.5 g/s with
an exit speed of 80.0 m/s. The car has a mass of 400 g, including the CO2 cylinder. Starting from rest, what is
the car's initial acceleration?
a. 0.90 m/s
2
c. 9.0 m/s
2
b. 4.5 m/s
2
d. 36 m/s
2
____ 31. A 1 000-kg experimental rocket sled on level frictionless rails is loaded with 50 kg of propellant. It exhausts
the propellant in a 20-s "burn." If the rocket, initially at rest, moves at 150 m/s after the burn, what impulse is
experienced by the rocket sled?
a. 1.1 10
5
kgm/s c. 1.5 10
5
kgm/s
b. 1.6 10
5
kgm/s d. 1.9 10
5
kgm/s
____ 32. A 1 000-kg experimental rocket sled at rest on level frictionless rails is loaded with 50 kg of propellant. It
exhausts the propellant in a 20-s "burn." The rocket moves at 150 m/s after the burn. What average force is
experienced by the rocket during the burn?
a. 0.95 10
4
N c. 0.60 10
4
N
b. 0.75 10
4
N d. 0.35 10
4
N
____ 33. A helicopter stays aloft by pushing large quantities of air downward every second. What mass of air must be
pushed downward at 40.0 m/s every second to keep a 1 000-kg helicopter aloft?
a. 120 kg c. 360 kg
b. 245 kg d. 490 kg
____ 34. At liftoff, the engines of the Saturn V rocket consumed 13 000 kg/s of fuel and exhausted the combustion
products at 2 900 m/s. What was the total upward force (thrust) provided by the engines?
a. 3.77 10
7
N c. 1.47 10
8
N
b. 7.54 10
7
N d. 2.95 10
8
N5
____ 35. A rocket of total mass M and with burnout mass 0.20 M attains a speed of 3 200 m/s after starting from rest in
deep space. What is the exhaust velocity of the rocket?
a. 1 000 m/s c. 3 000 m/s
b. 2 000 m/s d. 4 000 m/s
____ 36. Two masses collide and stick together. Before the collision one of the masses was at rest. Is there a situation
in which the kinetic energy is conserved in such a collision?
a. Yes, if the less massive particle is the one
initially at rest.
c. Yes, if the two particles have the same
mass.
b. Yes, if the more massive particle is the
one initially at rest.
d. No, kinetic energy is always lost is such a
collision.
____ 37. In an automobile collision, how does an airbag lessen the blow to the passenger? Assume as a result of the
collision, the passenger stops.
a. The air bag decreases the momentum
change of the passenger in the collision.
c. The stopping impulse is the same for
either the hard objects or the airbag.
Unlike the windshield or dashboard, the
air bag gives some increasing the time for
the slowing process and thus decreasing
the average force on the passenger.
b. During the collision, the force from the
air bag is greater than would be the force
from the windshield or dashboard so the
passenger cannot hit the hard objects.
d. The airbag is there to insure the seatbelt
holds.
____ 38. Two masses m1 and m2, with m1 < m2, have momenta with equal magnitudes. How do their kinetic energies
compare?
a. KE1 < KE2 c. KE1 > KE2
b. KE1 = KE2 d. More information is needed.ID: A
1
Momentum
Answer Section
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. D
2. D
3. D
4. B
5. A
6. A
7. D
8. B
9. B
10. C
11. B
12. D
13. B
14. D
15. A
16. B
17. C
18. B
19. B
20. D
21. A
22. B
23. A
24. B
25. B
26. C
27. D
28. B
29. C
30. A
31. C
32. B
33. B
34. A
35. B
36. D
37. C
38. C
Multiple Choice Physics 101 Quiz
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
1) The work done by the centripetal force on an object with a mass of 1 kg moving with a constant velocity of 4 m/s into a circular path of radius 0.6 m for one full cycle is
A) 100.7 J B) 3.8 J C) 0 J D) 80 J
Answer: C
2) A truck has four times the mass of a car and is moving with twice the speed of the car. If Kt and Kc refer to the kinetic energies of truck and car respectively, it is correct to say that
A) Kt = 16Kc B) Kt = 4Kc C) Kt = Kc D) Kt = 1/2 Kc
Answer: A
Figure 7-4
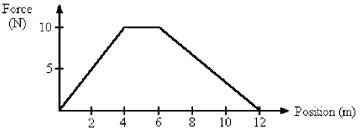
3) An object is under the influence of a force as represented by the force vs. position graph in Figure 7-4. What is the work done as the object moves from 6 m to 12 m?
A) 20 J B) 30 J C) 0 J D) 40 J
Answer: B
4) A car accelerates from rest to a speed of 20.0 m/s in 6.00 seconds. If the car weighs 16,000 N, what average power must the motor produce to cause this acceleration?
A) 128 kW B) 15.0 kW C) 54 .4 kW D) 219 kW
Answer: C
A mass of 1.0 kg is pushed against a spring with a spring constant of 25 N/m. As a result, the spring is compressed by 20 cm. The mass is then released.
5) What is the amount of work required to compress the spring?
A) 5.0 J
B) 0.20 J
C) 0.50 J
D) 10 J
Answer: C
6) An object of mass m is held at a vertical height h from ground level. It is then released and falls under the influence of gravity. Which of the following statements is true in this situation? (Neglect air resistance.)
A) The total energy of the object is decreasing.
B) The kinetic energy of the object is decreasing.
C) The total energy of the object is increasing.
D) The potential energy of the object is decreasing and the kinetic energy is increasing.
Answer: D
Figure 8-7
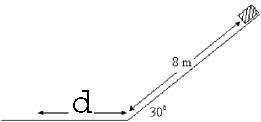
An object with a mass of 10.0 kg is at rest at the top of a frictionless inclined plane of height 8.00 m and an angle of inclination 30.0e with the horizontal. The object is released from this position and it stops at a distance d from the bottom of the inclined plane along a horizontal surface, as shown in Figure 8-7. The coefficient of kinetic friction for the horizontal surface is 0.400 and g = 10.0 m/ s to power of (exponent).
7) Refer to Figure 8-7. What is the kinetic energy of the object at the bottom of the inclined plane?
A) 400 J
B) 500 J
C) 700 J
D) 800 J
Answer: D
Figure 8-10
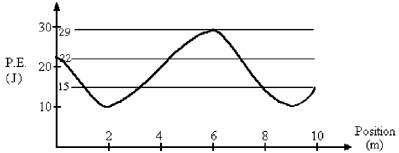
2-kg mass is moving along the x axis. The potential energy curve as a function of position is shown in Figure 8-10. The system is conservative. There is no friction.
8) Refer to Figure 8-10. If the object is at rest at the origin, what will be its speed at 9.0 m along the +x-axis?
A) 1.5 m/s
B) 2.5 m/s
C) 3.5 m/s
D) 4.5 m/s
Answer: C
9) A golf club exerts an average force of 1000 N on a 0.045-kg golf ball which is initially at rest. The club is in contact with the ball for 1.8 ms. What is the speed of the golf ball as it leaves the tee?
A) 35 m/s
B) 40 m/s
C) 45 m/s
D) 50 m/s
Answer: B
10) In a collision between two unequal masses, how does the impulse imparted to the smaller mass by the larger mass compare with the impulse imparted to the larger mass by the smaller one?
A) It is larger.
B) It is smaller.
C) They are equal.
D) The answer depends on how fast they are moving.
Answer: C
11) An elastic collision of two objects is characterized by the following.
A) Total momentum of the system is conserved.
B) Total kinetic energy of the system remains constant.
C) Both A and B are true.
D) Neither A nor B are true.
Answer: C
12) A uniform piece of wire, 20 cm long, is bent in a right angle in the center to give it an L-shape. How far from the bend is the center of mass of the bent wire?
A) 2.5 cm
B) 3.5 cm
C) 5.0 cm
D) 7.1 cm
Answer: B
13) How long does it take a wheel that is rotating at 33.3 rpm to speed up to 78.0 rpm if it has an angular acceleration of 2.15 rad/ s to power of (exponent)?
A) 20.8 s
B) 10.4 s
C) 2.18 s
D) 5.20 s
Answer: C
14) A Ferris wheel with a radius of 12.0 m rotates at a constant rate, completing one revolution in 30.0 s. What is the apparent weight of a 60.0-kg passenger when she is at the top of the wheel?
A) 589 N
B) 557 N
C) 615 N
D) 325 N
Answer: B
15) A dumbbell-shaped object is composed by two equal masses, m, connected by a rod of negligible mass and length r. If I1 is the moment of inertia of this object with respect to an axis passing through the center of the rod and perpendicular to it and I2 is the moment of inertia with respect to an axis passing through one of the masses we can say that
A) I1 = I2
B) I1 > I2
C) I1 < I2
D) There is no way to compare I1 and I2.
Answer: C
16) A solid disk, a hoop, and a solid sphere are released at the same time at the top of an inclined plane. They all roll without slipping. In what order do they reach the bottom?
A) disk, hoop, sphere
B) sphere, disk, hoop
C) hoop, sphere, disk
D) hoop, disk, sphere
Answer: B
17) The rotating systems shown in the figure differ only in that the two identical movable masses are positioned a distance r from the axis of rotation (left), or a distance r/2 from the axis of rotation (right). If you release the hanging blocks simultaneously from rest,

A) the block at left lands first.
B) the block at right lands first.
C) both blocks land at the same time.
D) it is impossible to tell which block reaches the bottom first.
Answer: B
18) A 3.00-m-long ladder, weighing 200 N, rests against a smooth vertical wall with its base on a horizontal rough floor, a distance of 1.20 m away from the wall. If the center of mass of the ladder is 1.40 m from its base, what frictional force must the floor exert on the base of the ladder in order for the ladder to be in static equilibrium?
A) 93.3 N
B) 130 N
C) 40.7 N
D) 102 N
Answer: C
19) A puck moves on a horizontal air table. It is attached to a string that passes through a hole in the center of the table. As the puck rotates about the hole, the string is pulled downward very slowly and shortens the radius of rotation, so the puck gradually spirals in towards the center. By what factor will the puck's angular speed have changed when the string's length has decreased by 1/2?
A) 2
B) 4
C) sqrt(2)
D) 1
Answer: B
Figure 11-6
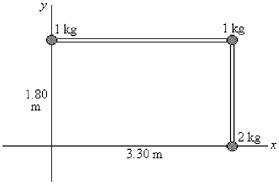
20) The L-shaped object shown in Figure 11-6 consists of the masses connected by light rods. How much work must be done to accelerate the object from rest to an angular speed of 3.25 rad/s about the y-axis?
A) 374 J
B) 173 J
C) 42.2 J
D) 27.4 J
Answer: B
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)